

You can configure AX Server to use the PostgreSQL or Oracle database server and one or two physical machines.
You can deploy AX Server across one or more servers, and you can select between two database server options: PostgreSQL or Oracle.
| Configuration 1: single server | Configuration 2: multiple servers | Configuration 3: multiple servers |
|---|---|---|
| AX Server and a PostgreSQL database server installed on the same physical server. | AX Server and a PostgreSQL database server installed on separate physical servers. | AX Server and an Oracle database server installed on separate physical servers. |

|

|

|
| [PDF] Installing AX Server with Postgres | [PDF] Installing AX Server with Postgres (multi-server) | [PDF] Installing AX Server with Oracle |
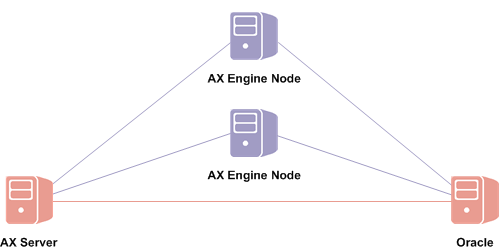
All three configurations support one or more optional AX Engine Node instances on one or more additional physical servers. Each instance of AX Engine Node increases analytic processing capability by running queued jobs.
AX Engine Nodes must be installed on a dedicated server or servers and cannot be installed on the same physical machine as AX Server. For more information, see Configuring AX Engine Nodes
Tip
An alternative to adding engine nodes is to adjust the processing capability of AX Server by increasing the number of concurrent jobs that the server can run. To adjust the number of jobs running on AX Server, change the value of the Jobs (max) field of the AX Server Configuration web application. For more information, see AX Server settings.
| Single server | Multi-server |
|---|---|
| Smaller implementations | Larger implementations |
| Low to medium number of concurrent users and scheduled jobs | High number of concurrent users and scheduled jobs |
| Low complexity and scale | High complexity and scale |
When choosing a configuration, consider your organization's:
Note
Your ACL account representative, or ACL Support Services, in conjunction with your IT department, can help you choose the most appropriate configuration.