Assurance in a nutshell
Learn about the different types of assurance and the components involved in displaying each calculation in Projects.
Types of assurance
| Type | Description | Why it is important |
|---|---|---|
| Assurance for risk |
A calculation-based process, with the final result that is represented by a value (a percentage). Assurance allows you to benchmark how well an organization is doing in mitigating risk so that resources can be allocated appropriately. |
It shows your organization's confidence in risk being effectively mitigated. |
| Assurance for compliance |
A calculation-based process, with the final result that is represented by a value (a percentage). Assurance represents your organization's confidence in requirements being met. |
It shows how much work needs to be done to comply with a specific standard or regulation within a compliance map. |
How it works
First, you create relationships between risks / requirements and controls and specify control weights to indicate the percentage of the risk or requirement that the control mitigates. Then, you perform walkthroughs and tests to record whether controls pass or fail.
Projects automatically averages and aggregates the testing results, allowing you to report on assurance for risk (per objective, project, or framework), and assurance for compliance (per standard or regulation).
Note
- Interface terms are customizable, and fields and tabs are configurable. In your Diligent One organization, some terms, fields, and tabs may be different.
- If a required field is left blank, you will see a warning message: This field is required. Some custom fields may have default values.
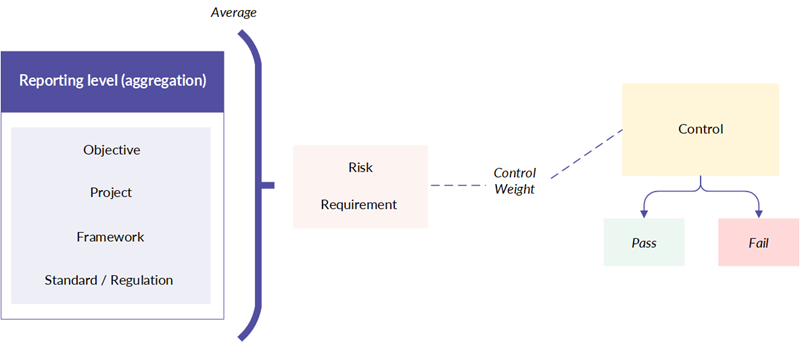
Risks and requirements
You create relationships between risks / requirements and controls to define which controls are designed to mitigate each risk / requirement.
- Assurance for risk you identify operational risks, specify risk scores, and associate risks to controls in your risk control matrix.
- Assurance for compliance you identify applicable requirements to your organization and map framework controls to requirements in your compliance map.
Controls
For each control you define, you perform walkthroughs to evaluate the design effectiveness of the control, and tests to evaluate operating effectiveness of the control. If any one walkthrough or testing round fails, the control is marked as "failed" and is subtracted from the overall assurance score.
Control weight
For each control you define, you can specify a control weight to express the percentage of the risk or requirement that the control mitigates.
- Assurance for risk you specify a control weight when you associate a control with a risk.
- Assurance for compliance you specify a control weight within the compliance map when you map a framework control to a requirement.
Reporting level
As you complete walkthroughs and tests, Projects automatically aggregates and averages the testing results, and allows you to report on the following:
- Assurance for risk report on overall assurance per objective, project, or framework.
- Assurance for compliance report on compliance progress per standard or regulation.
For more granular level reporting, you can do the following:
- Assurance for risk report on individual inherent risk and residual risk scores per risk.
- Assurance for compliance report on assurance per requirement.
Examples
Assurance for risk
Scenario
You have one risk associated with two controls in a project. The project contains one walkthrough per control. You specify that each control has a weighting of 100%. When you test the controls, you note that Control 1 is operating effectively and Control 2 is not operating effectively.
| Risk | Control | Control weight | Walkthrough: Operating effectively? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk 1 | Control 1 | 100% | Yes |
| Control 2 | 100% | No |
Result
Overall assurance for the project is 0% because if any one walkthrough or testing round for a control fails, the control is marked as "failed". The control is taken into account as part of the residual risk score, and it is subtracted from the overall assurance score.
- If Control 2 was not tested, overall assurance for the project still remains at 0% because a walkthrough must pass, OR at least one of the applicable testing rounds must pass while the other testing rounds have not been tested, to mark the control as "passed".
- If Control 2 was marked as "operating effectively", overall assurance for the project becomes 100% because all walkthroughs have passed.
There are no partially effective controls in Projects — controls are either effective or ineffective. If you identify a low impact issue that, in your judgment, does not affect the effectiveness of the control, you can mark the control as still "effective", and log a minor issue.
Assurance for compliance
Scenario
You have one requirement mapped to two framework controls in your compliance map. You specify different weights for each framework control. When you test the controls, you note that Control 1 is operating effectively and Control 2 is not operating effectively.
| Requirement | Framework control | Control weight | Operating effectively? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement 1 | Framework Control 1 | 50% | Yes |
| Framework Control 2 | 100% | No |
Result
Assurance for the standard is 50% because only one of the controls is operating effectively. If any one walkthrough or testing round for a control fails, the control is marked as "failed" and is subtracted from the assurance score.
- If Control 2 was not tested, assurance for the standard still remains at 50% because a walkthrough must pass, OR at least one of the applicable testing rounds must pass while the other testing rounds have not been tested, to mark the control as "passed".
- If Control 2 was marked as "operating effectively", assurance for the standard becomes 100% because all walkthroughs and tests have passed.
Next steps
For detailed information on assurance, see the following topics:
| Topic | Contains |
|---|---|
| Getting started with assurance for risk | Detailed conceptual information on how assurance for risk works |
| Assurance components | Detailed information on the components that affect assurance for risk |
| Calculating assurance for risk |
Detailed conceptual information on calculating assurance for risk and an example of reporting on assurance for a single project and across multiple projects |
| Calculating assurance for compliance | Detailed conceptual information on calculating assurance for compliance and an example of reporting on assurance for a single standard |