Demonstrating compliance
With thousands of industry standards, internal policies, and ever-changing regulatory requirements, optimizing coverage in a changing compliance landscape can be daunting. It's vital that organizations put the necessary processes and technology in place to appropriately identify, rationalize, prioritize, and mitigate compliance risk. In this article, we discuss how to demonstrate assurance over a compliance program using the Projects, Frameworks, and Compliance Maps apps.
This article illustrates how to demonstrate compliance with the COBIT® 5 Framework. However, the same workflow can also be applied to demonstrate compliance with:
- regulations applying to financial institutions, such as Truth-in Lending, Anti-Money Laundering, or Depository Insurance
- other IT security frameworks, such as ISO or NIST
- Data Privacy regulations, such as the EU GDPR, GLBA, HIPAA, and FERPA
- regulations applying to government or higher-education, such as Uniform Grant Guidance, Single Audit, or Title IV
What does it mean to demonstrate compliance?
Demonstrating compliance means that an organization is committed to conducting business in conformity with the regulations and standards that apply to them.
Demonstrating compliance isn't just about showing that compliance requirements have been met, but also demonstrating how the requirements are met, and what structured programs are in place to enable ongoing compliance.
Where do I demonstrate compliance?
At Diligent, we use the Projects, Frameworks, and Compliance Maps apps to attest to assessors and other interested third parties that a strong control environment exists. Our compliance program prevents us from exposing the organization to regulatory enforcement action and data breaches. It also allows us to collaborate with business stakeholders that are required to comply with various regulations and standards.
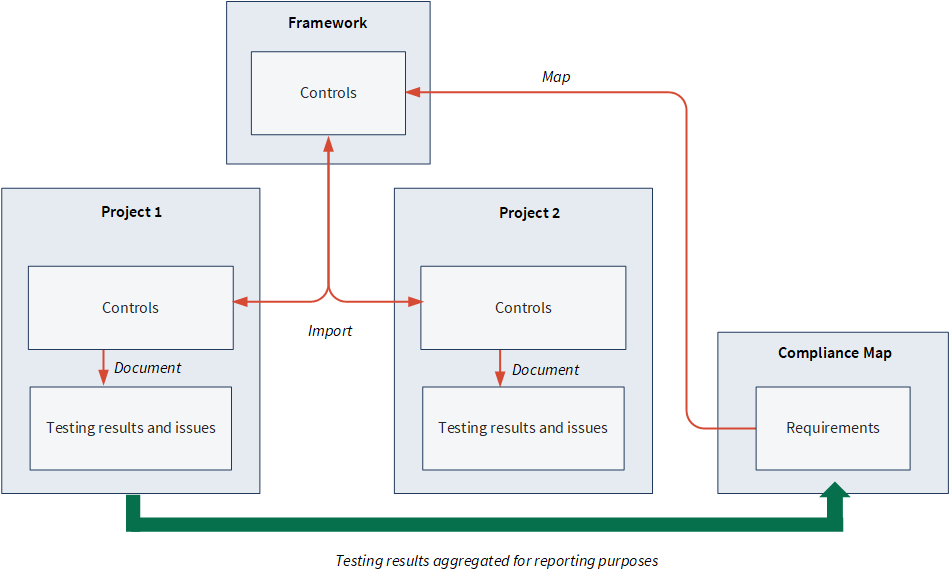
The big picture
- Compliance Maps is where compliance teams can perform the initial compliance gap and risk assessment by mapping requirements to existing organizational controls contained in frameworks.
- Frameworks are used in connection with Compliance Maps to centrally capture the master relationship between requirements and controls, manage changes to controls in an evolving regulatory and business environment, and build individual projects.
- Projects is used to test the design and operational effectiveness of the control, and capture issues. If necessary, you can sync changes back up to a framework from a project as well.
When you map requirements to framework controls, testing results and issues from multiple projects are automatically aggregated to the Compliance Map, allowing you to track and report on compliance status in real-time.
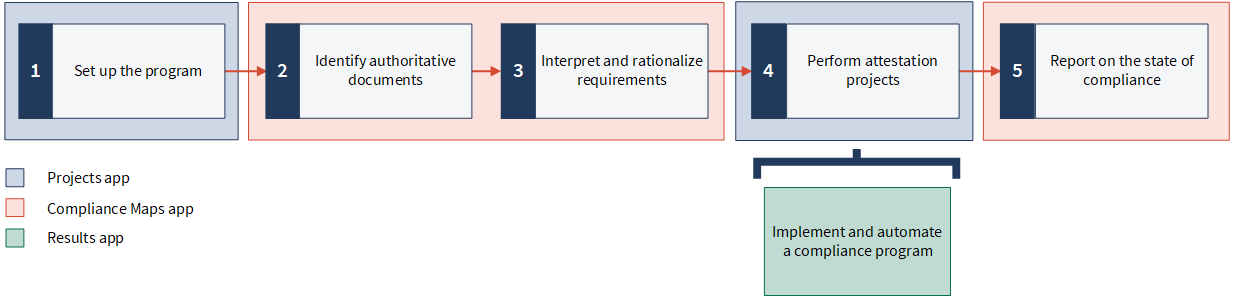
Steps
Ready for a tour?
Let's take a closer look at these features in the context.
1. Set up the program
The first step in building out your compliance program is setting up your projects and frameworks. You can create frameworks to manage a structured set of information and use frameworks to build multiple projects. You can also customize the terminology and labels in the projects according to your organization's standards, and sync changes back to a framework from a project if you want to apply those changes to other projects.
Set up projects and frameworks
Frameworks are helpful for reducing manual efforts involved in setting up projects, and can be used to centrally manage information in evolving regulatory and business environments.
Example
Scenario
You are an IT compliance professional that owns three projects:
- GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment
- Cybersecurity Review
- IT General Controls Review
You recently recognized that similar risks and controls can apply to the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects.
Previously, you created a project from a project template called IT General Controls Review (IA Context). You want to use this template to create a single set of risks and controls that can be used in both the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects.
Process
Help topics
First, you create a blank GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment – you'll be using this later to develop a compliance risk inventory and conduct the initial phases of the compliance risk assessment.
Then, you create a new framework called IT General Controls Framework, and import the objectives (containing risks and controls) from the project template to the framework.
Finally, you import the objectives from the framework into the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects.
Result
The GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment is set up, and you can begin defining the audit and risk areas that are relevant to the organization.
The objectives, risks, and controls in the IT General Controls Framework are linked to the objectives, risks, and controls in the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects. You can now update the projects as needed, optionally apply those updates back up to the framework, and also ensure that updates made in the framework propagate to the appropriate projects by syncing projects with frameworks.
Configure project terminology
Terminology can vary widely between different types of projects, and also between organizations performing the same types of projects. Organizations can configure different project types so that the terminology used by each team is reflected in the relevant projects.
Example
Scenario
You want to ensure that the terminology displayed in the GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment aligns with your organization's preferred lexicon.
Process
Help topic Customizing terms, fields, and notifications
You navigate to the Compliance Investigation / Examination project type, and configure the following terms on each tab:
Risk and Procedures tab:
- Term for project plan → Compliance Risk Inventory
- Abbreviation for project plan → CRI
- Term for risk → Requirement
- Term for procedure → Planned Project
- Term for procedure ID → Planned Project ID
Execute Procedures tab:
- Term for execute procedures tab → Prioritized Projects
- Term for execute procedure → Prioritized Projects
Result
The custom terms are applied to the GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment:

2. Identify authoritative documents
Once you have set up your projects and frameworks, the next step is to identify the authoritative documents that are applicable to your organization, and include these documents in your Compliance Map.
Authoritative documents may take the form of regulations published by a regulatory body, such as a government, professional standards published by a professional practice body or trade association, or internal policies or procedures published by executive management.
Tip
Certain standards and regulations are available as part of your regular subscription plan. Additional standards and regulations are available by subscribing to content suites offered through the Content & Intelligence Gallery , a central repository for industry-specific content that can be used in Diligent products.
Example
Scenario
Your organization needs to comply with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (EU) 2016/679, a regulation that provides requirements to protect personal data, which can include typical personal or account data that identifies a person.
You recognize that GDPR can be satisfied by adopting existing best practices, such as COBIT, ITIL, NIST, and ISO. To adopt the elements required to meet GDPR requirements, your organization has decided to leverage the COBIT® 5 Framework, a comprehensive IT audit framework that helps enterprises create optimal value from IT by maintaining a balance between realizing benefits and optimizing risk levels and resource use.
Process
Help topic Importing standards and regulations
You import the COBIT® 5 Framework to your Compliance Map.
Result
Your Compliance Map is populated with a list of requirements:

3. Interpret and rationalize requirements
Once you have imported the relevant content into your Compliance Map, you can perform a compliance risk assessment, and begin the process of interpreting and rationalizing requirements. You have full control over the internal compliance process, including where on the spectrum you want to fall, and the level of compliance coverage you want to achieve.
Perform a compliance risk assessment
Organizations that implement high quality compliance programs engage in a systematic identification and assessment of risks. Compliance risk assessments provide the means of assessing standard or regulation applicability, prioritizing the standards or regulations that should be managed first, and informing which requirements may be applicable to the organization.
Example
Scenario
Before you can interpret and rationalize requirements in the COBIT® 5 Framework, you need to develop a compliance risk inventory to identify and rank risks, and specify which planned projects will serve to address or minimize the key risk areas.
The compliance risk inventory will list risks that the organization has faced in the past, or is expected to face in the future. Risks should be ranked based on impact and likelihood on a three-point scale (1-Low, 2-Medium, 3-High).
Process
Help topics
Within the GDPR Compliance Risk Assessment, you define the first requirement: Report Data Breaches. In the Report Data Breaches requirement, you define and assess the first risk that is in scope for your organization:
DP-1: Failure to protect data systems against misuse or unauthorized access by employees Employees can breach systems with the intent to steal data or obtain personal data about co-workers.
- Impact Medium
- Likelihood High
Finally, you specify that two planned projects that will cover the risk area:
- Cybersecurity Review
- IT General Controls Review
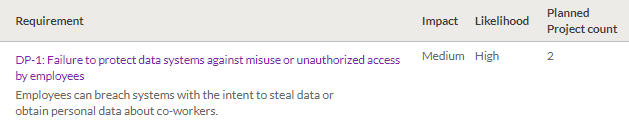
Result
The first risk area of focus is assessed. The compliance risk assessment will help to determine which requirements within the COBIT® 5 Framework are applicable to the organization.
Identify applicable and covered requirements
Once you have completed the compliance risk assessment, you can begin the process of identifying applicable and covered requirements.
There are two primary methods you can use to interpret and rationalize requirements:
- Address everything exactly as the requirement dictates and implement accordingly reduces non-compliance risk, but increases the burden to implement and manage compliance
- Interpret requirements by applying professional judgment and rationalize optimal coverage sufficient for the organization reduces the burden of compliance, but may increase non-compliance risk to the organization
Tip
A good compliance strategy attempts to rationalize the required process and control changes in order to maximize compliance coverage by leveraging as many existing processes as possible.
Example
Scenario
The results of the compliance risk assessment now allow you to interpret and rationalize requirements within the COBIT® 5 Framework. You need to apply professional judgment and rationalize optimal coverage that's sufficient for the organization.
Process
Help topic Creating a compliance map
In Compliance Maps, you mark each requirement that is applicable to your organization, provide a rationale stating why the requirement is applicable.
You capture information for requirement DSS05.04 Manage user identity and logical access as follows:
- Applicable Yes
- Covered Yes
- Rationale As a result of the compliance risk assessment, this requirement has been identified as applicable to the organization.
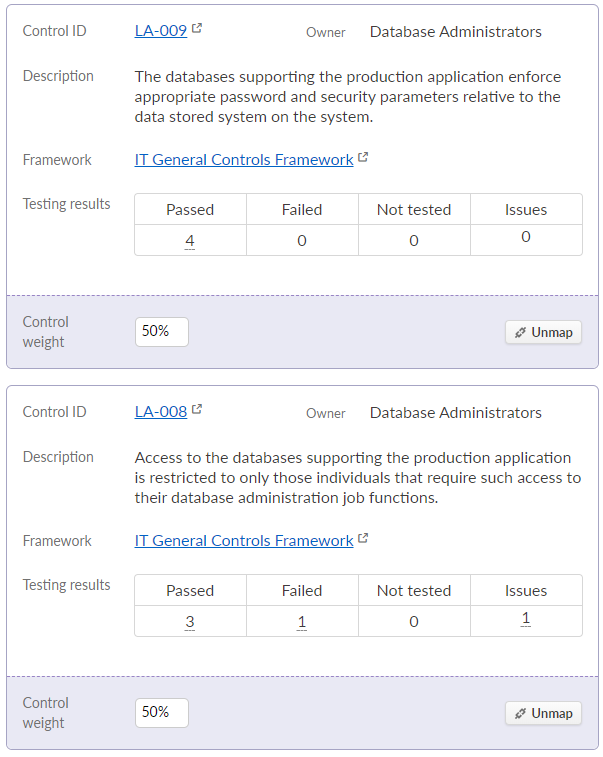
Finally, you map the following existing controls to requirement DSS05.04:
| Control ID | Control Description | Control Weight |
|---|---|---|
| LA-008 | Access to the databases supporting the production application is restricted to only those individuals that require such access to their database administration job functions. | 50% |
| LA-009 | The databases supporting the production application enforce appropriate password and security parameters relative to the data stored system on the system. | 50% |
Result
You have addressed everything exactly as the requirement dictates and implemented two direct controls accordingly. Any testing results and issues associated with the controls are aggregated to the Compliance Map for reporting purposes.
4. Perform attestation projects
Using frameworks as a centralized repository of information, you can execute attestation projects to conduct operational risk assessments, work with control owners to centrally track compliance performance across all objectives, and capture issues. Performing attestation projects allows you to benchmark how well your organization is doing in managing compliance risk and requirements.
Perform operational risk assessments
Performing an operational risk assessment is a process that involves determining how much risk an organization faces. You can develop a common set of assessment criteria that can be used across operating segments, entities, or business units, and score operational risks based on the defined scoring framework.
Tip
To avoid manually scoring operational risks, you can use Assessment Drivers to automate different risk assessments. You can link a metric created in the Results app to a risk assessment in Projects in order to inform the assessment, and auto-populate inherent risk scores based on pre-defined metric ranges.
Example
Scenario
Your organization has a mature and refined operational risk assessment process, and evaluates risk across two dimensions (Likelihood and Impact) on a three-point scale:
- 1 - Low
- 2 - Medium
- 3 - High
Now, you need to evaluate the inherent risk score to determine the raw risk the organization faces if no controls or other mitigating factors have been put in place.
Process
Help topics
You capture the following information in the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects:
| Project | Risk | Impact | Likelihood |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cybersecurity Review | Risk LA-: Untitled Risk Individuals job responsibilities to maintain appropriate access restriction on data are not adequately clear or actionable. | 2 - Medium | 1 - Low |
| IT General Controls Review | 2 - Medium | 3 - High |
Result
The inherent risk assessment is completed. Inherent risk scores are aggregated to the framework for reporting purposes.
Document and evaluate controls
Control owners can help to document the existence of controls in place and evaluate their effectiveness through attestation and / or attachment of evidence, define action plans to implement missing controls to address instances of non-compliance, or explain why a control is not necessary.
Tip
Frontline staff in an organization can use the Mission Control app to manage the controls they have access to, outside of the Projects app. Mission Control is an app that presents control information from Projects in a simplified and centralized view.
Example
Scenario
Now that you have assessed inherent risk, you also want to be able to determine the residual risk, or how much risk remains after controls have been put in place.
Process
Help topics
- Executing procedures and testing controls
- Tracking assurance using frameworks
- Creating a compliance map
You capture the following information and test the design and operational effectiveness of each control in both the Cybersecurity Review and IT General Controls Review projects:
Project: Cybersecurity Review
-
Risk : LA-: Untitled Risk -
Controls :- LA-008
Control Attributes :Description : Access to the databases supporting the production application is restricted to only those individuals that require such access to their database administration job functions.Weight : 50%
- Walkthrough
Results : Designed Appropriately Testing Results : Operating Effectively
- LA-009
Control Attributes :Description : The databases supporting the production application enforce appropriate password and security parameters relative to the data stored on the system.Weight : 50%
- Walkthrough
Results : Designed Appropriately Testing Results : Operating Effectively
- LA-008
Project: IT General Controls Review
-
Risk : LA-: Untitled Risk -
Controls :- LA-008
Control Attributes :Description : Access to the databases supporting the production application is restricted to only those individuals that require such access to their database administration job functions.Weight : 50%
- Walkthrough
Results : Designed Appropriately Testing Results : Exception(s) Noted
- LA-009
Control Attributes :Description : The databases supporting the production application enforce appropriate password and security parameters relative to the data stored on the system.Weight : 50%
- Walkthrough
Results : Designed Appropriately Testing Results : Operating Effectively
- LA-008
Result
Testing results associated with the control are aggregated to the framework and Compliance Map for reporting purposes:
Capture issues and actions
You can capture and assign flagged issues for remediation throughout the compliance review process, and delegate issues to control or issue owners to update the status and related action plans. You can also assign actions to any stakeholder for easy tracking, evidence capture, and resolution.
Example
Scenario
Since one of the control tests failed in the IT General Controls Review, you need to note the exception by logging an issue. You also want to create a specific follow-up measure that is associated with an identified issue, and assign it to the appropriate staff member.
Process
Help topics
You document the following issue and actions in the IT General Controls Review:
Issue
- Title/Headline Unauthorized employees may have access to critical systems
- Description There is no process in place to ensure that only authorized employees have access to critical systems
- Owner IT Manager
- Issue Type Deficiency
- Date Identified Date
- Severity High
- Published Published
Action
- Title Monitor privileged access to critical systems on a regular basis
- Owner IT Manager
- Description Monitor production access logs and compare logged events with a sanctioned user list
- Due Date Date
- Status Opened
- Priority High
Result
The issue and action are captured. At a later date, Audit can review the remediation plan, and document retesting results to determine whether or not the issue has been truly remediated.
5. Report on the state of compliance
Ultimately compliance is the outcome of running a well-managed and well-controlled program. Compliance Maps provides the ability for all three lines of defense to quickly gain insight into the work each department is doing, and view aggregated information in real-time.
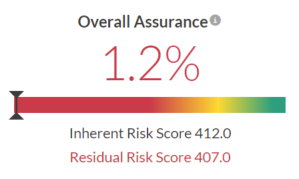
To demonstrate compliance progress, you can score compliance assurance with a single, overall metric (Coverage). This metric gives management an instant understanding of the degree to which the organization is compliant by regulation, business process, or entity. You can also, at any time, generate real-time reports that communicate the status of various control areas as well as the program's progress as a whole.
Example
Scenario
You need to track overall how well your organization is doing in mitigating compliance risk so that resources can be allocated appropriately. Luckily, the testing results and issues you captured in the attestation projects are aggregated to your Compliance Map, allowing you to track and report on compliance status in real-time.
Process
Help topic Creating a compliance map
You open Compliance Maps and view the aggregated and summarized information:
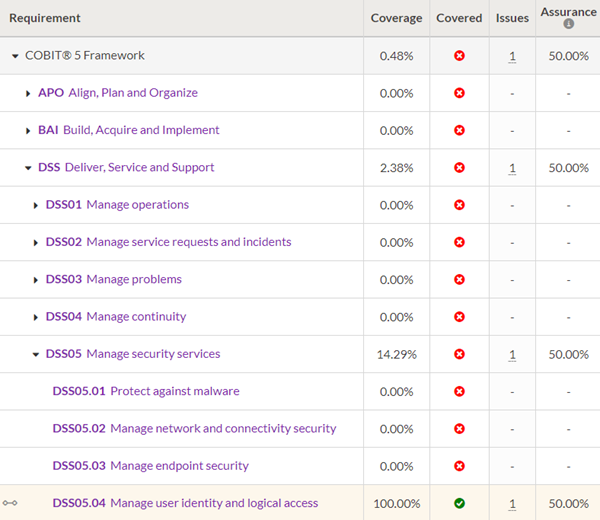
To obtain further details about DSS05.04, you click the requirement and view the mapped controls and aggregated testing results:
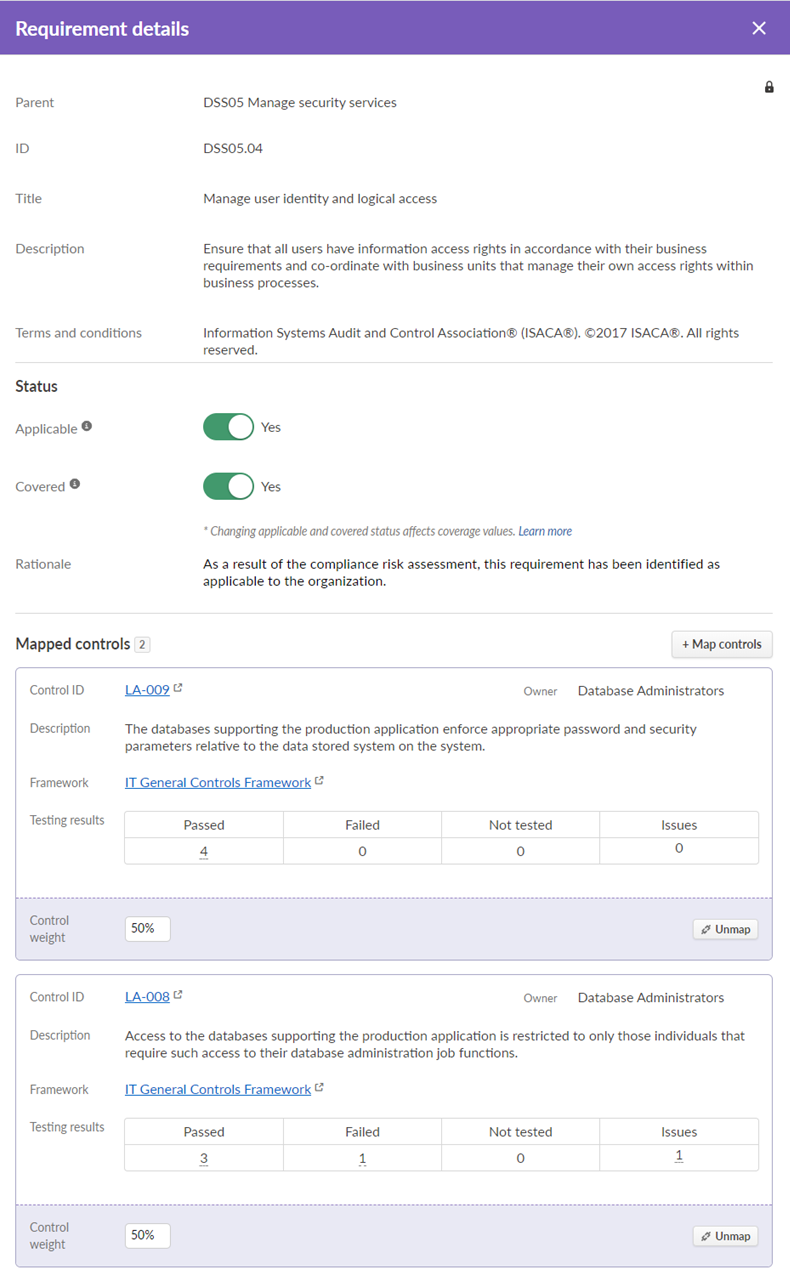
To demonstrate compliance progress, you share the Coverage metric with management, and export the Excel report. This provides management with an instant understanding of the degree to which the organization is compliant with the COBIT® 5 Framework.

Result
You quickly get insight into the current state of compliance for your organization.
What's next?
Learn how to implement and automate a compliance program
The Results app allows evaluators to capture incidents via data analytics, define triggered workflows for managing incidents, perform root cause analysis and remediation activities, and close cases once they are ready for reporting.
To find out more, see Implementing a compliance program.